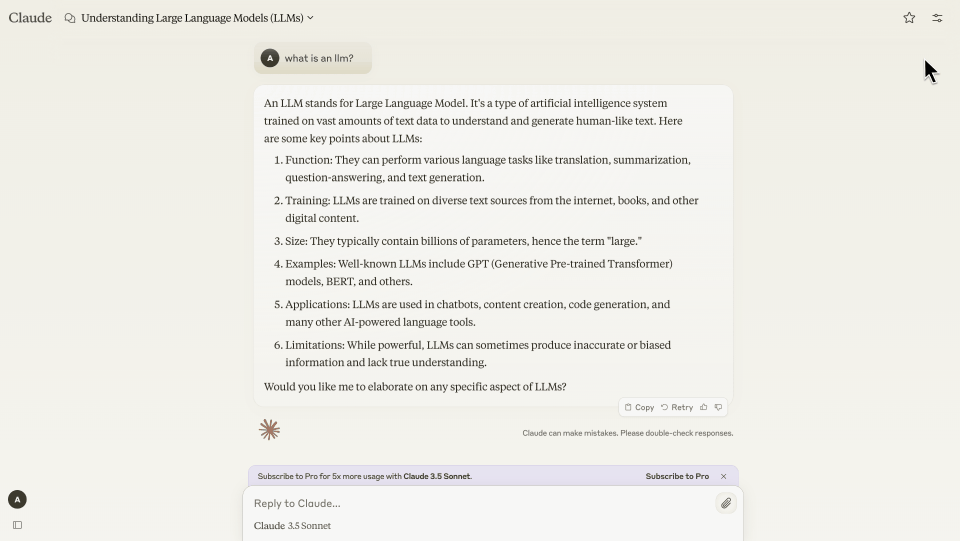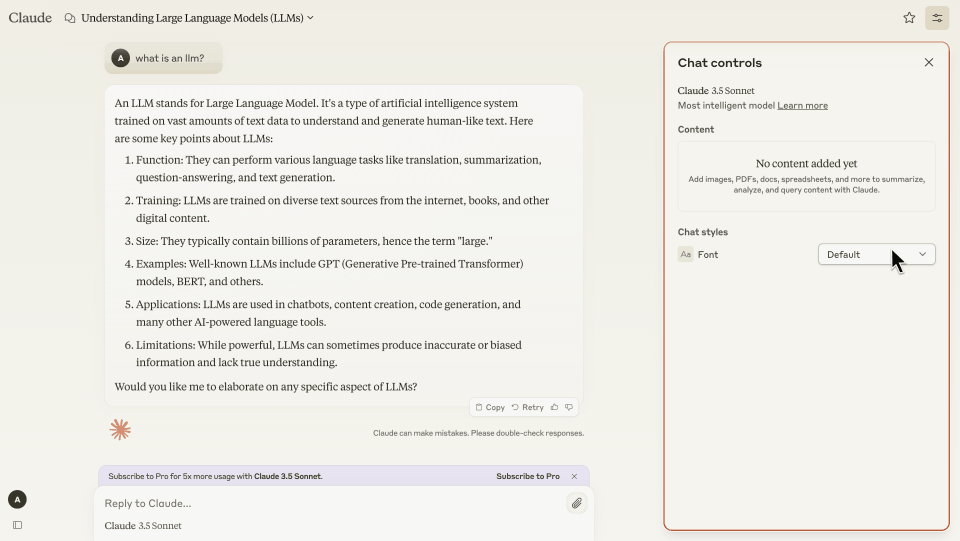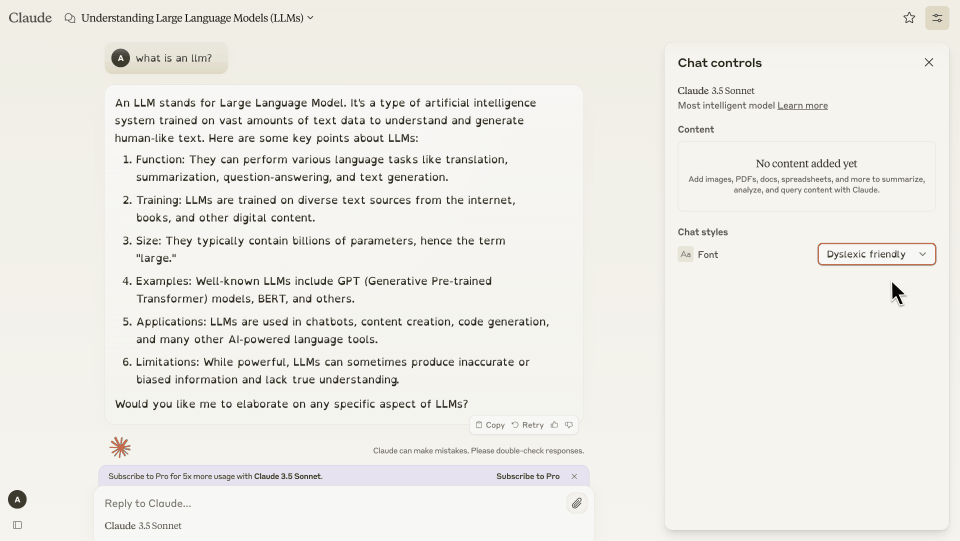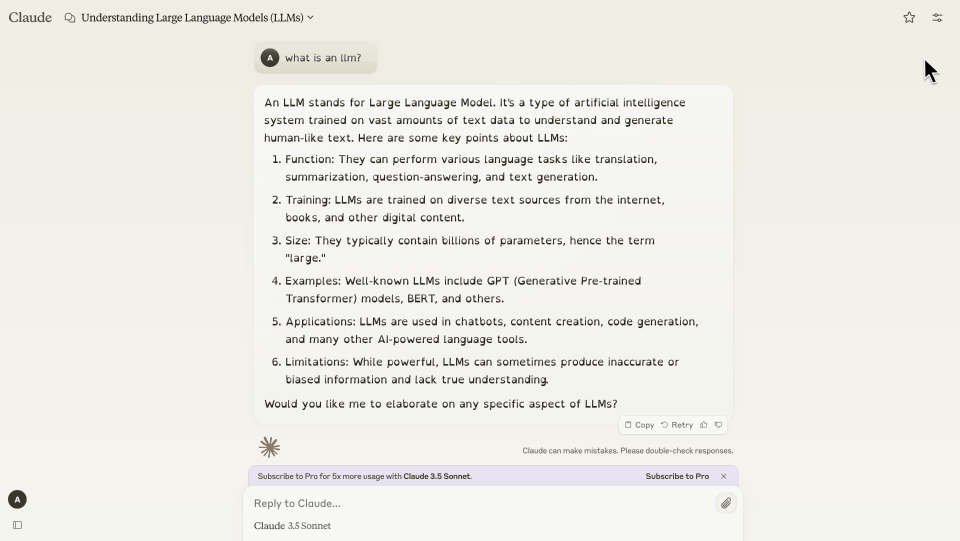
In developing a new conversational tool of our own, we embarked on a discovery phase that involved research into AI-powered conversational design and an analysis of the leading players in the industry. Through this process, we gained valuable insights into the best practices, trends, and user expectations surrounding conversational AI tools. Here are some of the key insights we discovered during the process.
Scale with purpose
Xwerx has built a number of successful partnerships by embedding our consultants with client teams. This has helped our clients to scale quickly to fulfill their book of work with speed and purpose.
Read Article